Unlocking the Power of Fixed Income
Episode 4
Understanding Bond Pricing – Why Do Bond Prices Fluctuate?
Introduction
Bond prices aren’t static—they fluctuate daily based on interest rate movements, credit risk, inflation expectations, market liquidity, and central bank policies.
Many investors focus on a bond’s coupon rate and yield, but understanding the drivers of bond price movements is essential for navigating fixed-income markets effectively.
In this episode, we’ll explore:
📌 How interest rates dictate bond pricing
📌 The impact of credit risk & bond ratings
📌 How inflation expectations erode bond value
📌 Why liquidity and demand affect bond pricing
📌 The role of central banks in shaping the yield curve
By the end, you'll have a clear grasp of bond pricing mechanics and strategies to position your portfolio accordingly.
1. Interest Rates – The Primary Driver of Bond Prices
The inverse relationship between bond prices and interest rates is the most fundamental concept in fixed-income investing. As interest rates fluctuate, bond prices adjust so that their yield aligns with prevailing market conditions.
📌 How It Works:
✔ Higher Interest Rates → Bond Prices Drop
✔ Lower Interest Rates → Bond Prices Rise
✔ Newly issued bonds adjust coupon rates to reflect new market conditions, so existing bonds must reprice to remain competitive.
📌 Example: The Impact of Changing Interest Rates
You own a 5-year bond with a 5% coupon rate, meaning it pays $50 per year per $1,000 invested.
Scenario 1: Interest Rates Rise to 6%
✔ Newly issued 5-year bonds now offer a 6% coupon ($60 per $1,000).
✔ Your 5% bond becomes less attractive.
✔ To compensate, its price drops below $1,000 so that its yield aligns with the market’s 6% rate.
Scenario 2: Interest Rates Fall to 4%
✔ Newly issued bonds now offer a 4% coupon ($40 per $1,000).
✔ Your existing 5% bond is now more attractive.
✔ Its price rises above $1,000 as investors seek higher yields.
💡 Key Takeaway:
- Bond prices and interest rates move inversely—when rates rise, bond prices fall, and when rates fall, bond prices rise.
- Longer-maturity bonds experience greater price swings (a concept known as duration risk).
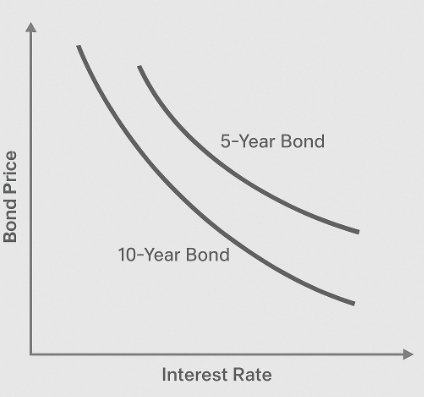
Figure 1: The Inverse Relationship Between Interest Rates and Bond Prices
This figure illustrates the fundamental inverse relationship between interest rates and bond prices. As interest rates increase (moving along the x-axis from left to right), bond prices decrease (moving down the y-axis). Two curves are shown:
-
5-Year Bond Curve – This line is relatively flatter, indicating that shorter-duration bonds are less sensitive to interest rate changes.
-
10-Year Bond Curve – This line is steeper, demonstrating that longer-duration bonds experience greater price fluctuations in response to interest rate shifts, a concept known as duration risk.
The diagram emphasizes how rising interest rates diminish the value of existing bonds (since new bonds offer higher yields), while falling interest rates increase their value. This visual serves as a foundational concept in fixed-income investing.
2. Credit Risk – How Bond Ratings Influence Price & Yield
Not all bonds carry the same level of risk. The creditworthiness of the issuer determines a bond’s price and yield, as investors demand higher returns for riskier issuers.
📌 Bond Rating Categories: Understanding Credit Quality
Bond ratings, assigned by agencies like Moody’s, S&P, and Fitch, indicate an issuer’s ability to repay debt obligations:
✔ Investment-Grade Bonds (AAA to BBB-) – Lower risk, lower yields, favored by risk-averse investors.
✔ High-Yield Bonds (BB+ and below, aka "Junk Bonds") – Higher risk, higher yields, used by investors seeking greater returns.
📌 How Credit Ratings Impact Bond Pricing
✔ Downgrades Increase Risk → Bond Prices Fall
- A lower credit rating signals increased default risk, reducing demand.
- Lower demand pushes bond prices down, increasing yields.
📌 Example: Credit Downgrade & Price Decline
- A BBB- corporate bond is downgraded to BB+ (junk status).
- Institutional investors sell off the bond, causing prices to drop and yields to rise.
✔ Upgrades Improve Creditworthiness → Bond Prices Rise
- Stronger financials can lead to a credit upgrade, making a bond more desirable.
- Higher demand increases prices and lowers yields.
📌 Example: Credit Upgrade & Price Appreciation
- A BB-rated corporate bond is upgraded to BBB.
- Demand increases, pushing prices up and yields down.
💡 Key Insight: Wider credit spreads signal distress; narrower spreads indicate stability.
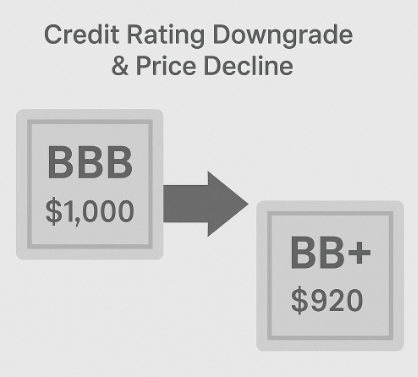
Figure 2: Credit Rating Downgrade and Its Impact on Bond Price
This figure visually demonstrates how a bond's price responds to a downgrade in credit rating. On the left, a bond with a BBB rating is priced at $1,000, indicating its status as an investment-grade security. A bold arrow points right, symbolizing a downgrade event. On the right, the bond now carries a BB+ rating—the first level of "junk" status—and is priced at $920.
The illustration highlights a key principle in fixed-income investing:
🔻 As credit ratings decline, perceived risk increases.
🔻 Higher risk leads to lower demand, which causes bond prices to fall and yields to rise.
This downgrade dynamic underscores why credit quality is a critical factor in bond valuation and investor decision-making.
3. Inflation Expectations – The Silent Bond Killer
Inflation is a bond investor’s biggest enemy because it erodes the purchasing power of future fixed coupon payments.
📌 Why Inflation Hurts Bonds
✔ Fixed coupons lose purchasing power when inflation rises.
✔ Investors demand higher yields to offset inflation risk.
📌 Example: Inflation's Impact on Bonds
Scenario 1: Inflation Rises from 2% to 5%
✔ Investors demand higher yields to compensate for inflation.
✔ Newly issued bonds adjust to higher rates, making existing bonds less attractive.
✔ Prices fall as investors seek inflation protection.
Scenario 2: Inflation Remains Low at 2%
✔ The bond’s real return remains stable, keeping demand strong.
✔ Prices remain stable or rise.
💡 Key Takeaway: Inflation-linked bonds (TIBs) hedge against purchasing power erosion.
4. Market Demand & Liquidity – Why Trading Activity Affects Bond Prices
Even bonds with similar ratings and yields can trade at different prices due to liquidity and market demand.
📌 Example: The COVID-19 Market Shock (2020)
- Investors rushed into U.S. Treasuries, causing prices to surge and yields to plummet.
📌 Example: The UK Gilt Crisis (2022)
- Excess bond issuance led to plummeting prices, requiring central bank intervention.
💡 Key Insight: Highly liquid bonds are easier to sell at fair market value, while illiquid bonds may require discounts to attract buyers.
5. The Role of Supply & Central Banks – Policy's Influence on Bond Markets
Bond supply and central bank actions heavily influence pricing and yields.
📌 Example: The Federal Reserve & U.S. Bond Markets
✔ 2020 QE Program → Fed purchases bonds, lowering yields.
✔ 2022-23 Rate Hikes → Bond prices plummet, yields surge.
💡 Key Insight: Central banks dictate yield trends—always monitor policy shifts.
📌 Final Takeaways: Mastering Bond Price Movements
✅ Interest rates drive bond prices – Higher rates lower prices, lower rates raise them.
✅ Credit risk influences yields – Higher risk demands higher yields.
✅ Inflation erodes real returns – Rising inflation lowers bond values.
✅ Liquidity affects pricing – Less liquid bonds trade at discounts.
✅ Central banks shape market conditions – Monetary policy influences supply, demand, and yields.
Coming Up Next…
Next, we’ll explore "The Role of Bonds in a Portfolio: Safety, Income, and Diversification", covering:
✔ Why bonds are essential for portfolio stability
✔ How bonds generate income and manage risk
✔ The diversification benefits of adding bonds to an investment strategy
🔔 Stay tuned for more fixed-income insights! 🚀